The Difference Between Bitcoin and Traditional Currencies
The relationship between Bitcoin and traditional currencies is a complex one. Bitcoin seeks to undermine the traditional way of dealing with money, so Bitcoin vs traditional money is a natural opposition. The difference of Bitcoin from…

The relationship between Bitcoin and traditional currencies is a complex one. Bitcoin seeks to undermine the traditional way of dealing with money, so Bitcoin versus traditional money is a natural opposition. This article outlines the main differences between the two.
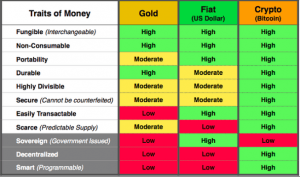
Traits of money
Over the history of humanity, money took many forms. There was barter, physical objects like rocks or shells, precious metals, bank notes, paper bills, digital money, and finally decentralized digital currencies like Bitcoin.
Over time, people noticed the most desirable traits that money should have. For the currency to be useful and convenient, it should be:
- Divisible — can be turned into smaller pieces for certain uses like paying a specific amount or micro-payments.
- Non-consumable — cannot be consumed for purposes other than an exchange of value.
- Portable — can be easily carried around.
- Durable — does not wear away or depreciate through time or in certain conditions.
- Secure — cannot be counterfeited.
- Easily transferable.
- Scarce — cannot be replicated without end.
- Fungible — each piece has the same value as its equivalent.
- Recognizable — it is recognized and accepted as a means of transaction.
Here is how gold, fiat currencies, and Bitcoin compare in the context of these traits.
The main difference of Bitcoin from traditional currencies lies in the fact that no one controls Bitcoin as it is decentralized. It allows Bitcoin to be an independent peer-to-peer money system that can function regardless of anyone’s wishes. It relies on the combined computing power of the network participants, each of which is equal among themselves — nobody is more or less important than the others. Additionally, it helps bring down the cost of using the system by ideally eliminating fees and transaction times, both of which banks need to stay in business.
No one can have an influence over your money and transactions you send or receive.
In contrast, fiat currencies rely on centralized entities like central banks, commercial banks, governments, payment processors like VISA or Mastercard, and other intermediaries. Any of those organizations have an authority to decide whether to approve your transaction, whether you can send money to certain people or organizations, or if the money you’re using is legal or not. These processes also include in-depth surveillance and data-sharing on everything you do with your money.
Other significant difference is that unlike fiat, Bitcoin is not sovereign. There is nothing backing Bitcoin, which means it’s value is not attached to any political or economic situation, and it can exist independently outside of the traditional system.
Last but not least, Bitcoin introduces a new dimension of programmability. It means that in the future, Bitcoin transactions can be attached to smart contracts or other programs that execute only after certain conditions are met. Such a feature would allow building additional solutions on top of bitcoin, such as reputation management systems, insurance contracts, or similar. Such contracts would not require any third-party intervention to execute. Essentially, it introduces a new dimension to the concept of traditional cash.
But Bitcoin isn’t backed by anything?
When asking how Bitcoin is different from the dollar, most people will tell you that it is because Bitcoin is not backed by anything. This is not entirely true: while Bitcoin indeed has nothing physical to back it, neither does the dollar. Historically speaking, up until 1971, most currencies were backed by a commodity, usually gold or silver. This is not the case anymore. Also, there is plenty of room for the argument that every Bitcoin is covered by the amount of electricity used while mining it.
All in all, unlike traditional currencies, Bitcoin:
- Has no central authority which claims it backs money.
- Is a subject to deflation due to artificial scarcity, while central banks can print more money anytime.
- Has every transaction forever recorded on an immutable public ledger.
- Requires transaction fees to be paid to miners, which serves like paying taxes to the government, except that taxes can be evaded while it is impossible to complete a transfer without paying fees on the blockchain.
- Transactions are done over the internet and include public addresses, while cash transactions are anonymous and leave no trail behind.
Many people call Bitcoin the next step in the evolution of money. Since we have never had money like Bitcoin before, it is normal to question the concept and compare it with traditional currencies.
Hopefully, now you know the key differences between Bitcoin and conventional money.
If you liked this article, don’t forget to share it with your friends.