Komodo Platform provides end-to-end blockchain solutions for developers in any industry. It uses a unique multi-chain architecture which gives every blockchain project a dedicated blockchain with independent infrastructure.
What Is Komodo (KMD)?

Komodo (KMD) is among the most innovative open-source blockchain platforms. It has introduced a delayed-Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism and the leading platform regarding atomic swaps technology.
The Komodo Platform integrates various impressive features and elements, like transaction privacy and anonymity, transparency, next-generation UXTO Smart Contracts, Bitcoin-level security, multi-chain sync, seamless blockchain interoperability, limitless scalability, a decentralized exchange with atomic swaps, and tools and services to secure or launch your independent blockchain or ICO.
Komodo is a second generation blockchain. Originally, it is a fork of privacy coin Zcash (ZEC), which itself is a fork of Bitcoin (BTC).

Due to these developments, Komodo’s native cryptocurrency KMD supports transparent, anonymous, private, and fungible transactions.
Komodo’s solutions are all about improving security, scalability, interoperability, and adaptability – the four pillars of blockchain technology.

Security is the most critical aspect of every blockchain project. Komodo uses the delayed-Proof-of-Work (dPoW) consensus algorithm. It protects the platform with the hashing power of the Bitcoin (BTC) network. With dPoW, attackers would need to overpower both KMD and BTC blockchains simultaneously.
Scalability. Every blockchain project must scale sooner or later. Unlike other enterprise solutions, Komodo enables each project to have their infrastructure and dedicated blockchain. All projects in the Komodo ecosystem can scale at any time and add additional blockchains to enhance performance.
Interoperability. Insufficient interoperability limits the practical use of various blockchain applications. Despite that, Komodo has already linked 95% of the existing blockchains. It uses blockchain federation tech which gives the means to seamless cross-chain interoperability with federated chains. Besides, Komodo blockchains can use atomic swaps to connect to other chains outside federation.
Adaptability. Inflexible solutions turn people aside from adopting blockchain technologies. Komodo is an open-source project recognized for its innovations and new features. Every project built with Komodo may create custom solutions that work for their circumstances.
All in all, the Komodo Platform cuts the barriers of entry for all innovative developers, blockchain startups, and existing businesses with complete end-to-end blockchain solutions.
Komodo (KMD) Team and History
At first, Komodo was known as a progeny of the Bitcoin Dark (BTCD), a privacy-oriented project which attempted to fix Bitcoin’s privacy issues. However, the project was abandoned and the official Bitcoin Dark to Komodo token swap period had already expired.
The Komodo Platform’s official birth is said to be February 21, 2016, when the project’s leader James Lee announced the “Declaration of Independence”:
“We the asset holders hereby declare our independence from any single blockchain.
An open and jointly developed specification on cross-chain atomic asset transfers will be developed. Any current or future blockchain is invited to join.
Each blockchain will need to not only promise protections for asset holder interests, they need to live up to them. Otherwise, all the assets will simply move to blockchains that do.….
This is an interop standards effort and it needs to be blockchain agnostic and asset centric.”
Like most privacy coins, Komodo’s team stayed anonymous for some time. However, as the project gains more traction, many team members have chosen to reveal their identities.
Komodo’s more than 50 people’s team is led by executive managers Kadan Stadelmann (CTO), Ben Fairbank (GM), Steve Lee (CMO), and Saddam Hossain (QA & Support). The founder James Lee, also known as “JL777” contributes as a core developer.
How Does Komodo (KMD) Work?
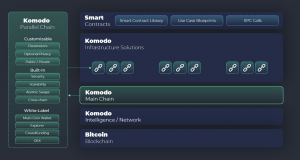
To have a better view of all technologies Komodo offers and how they come into play, they can be grouped into three distinct categories.
1. Secure Privacy Coin
Privacy and security are the foundational features of the Komodo platform. At first, the project inherited ZK-Snarks privacy from Zcash (ZEC). Then, Komodo’s founder James (aka JL777) has developed its security solution, the dPoW algorithm, which essentially takes snapshots of the Komodo blockchain and inserts them into Bitcoin’s chain every 10 minutes. Thanks to these snapshots, the Komodo blockchain can be restored to any point in time. A successful attack on the KMD blockchain would require overpowering both BTC and KMD chains simultaneously. Such standard constitutes the highest level of security in the industry.
2. The Blockchain Platform
Komodo grants developers unprecedented levels of autonomy and control. It offers an entirely independent blockchain with own infrastructure, which can remain unaffected by the events on the Komodo main chain. This is achieved using parallel chains, which works by making a separate copy of the Komodo blockchain.
All the new parallel chains are secured with the same dPoW consensus mechanism. In order to crack Komodo’s parallel chain, an attacker needs to overpower the Bitcoin network, Komodo’s chain, and the parallel chain altogether. Hence, developers can reap the benefits of an independent blockchain with its shared/dedicated network and predictable performance without any additional risks.
3. Komodo’s Decentralized Exchange (DEX)
Komodo’s decentralized exchange BarterDEX is at the center of the ecosystem. It serves as an intersection between all the chains.
Unlike other DEX’s that employ proxy tokens, BarterDEX is powered by atomic swaps. The goal of the exchange is to create the largest atomic swap network, which includes the parallel chains on the Komodo network and all external blockchains. According to the project developers, they have already successfully connected 95% of all blockchains, including most projects built on the Bitcoin and Ethereum protocols.
Here is a brief explanation of the key technologies behind Komodo.
The Delayed Proof-of-Work (dPoW) Consensus and Service
As stated earlier, Komodo uses the Delayed Proof-of-Work (dPoW) mechanism to secure its entire ecosystem. They even offer it as a service to protect other, more vulnerable blockchains, and currently serves (at least) five other projects: GameCredits (GAME), Kreds (KREDS), Einsteinium (EMC2), Hush (HUSH), and SUQA (SUQA). Any blockchain, regardless of its consensus mechanism or hashing algorithm, can adopt dPoW consensus.
The Komodo Platform’s dPoW system is attached to the Bitcoin’s Proof-of-Work network. It uses two types of nodes:
- Notary nodes. Like in delegated Proof-of-Stake systems (dPoS), dPoW stakeholders elect notary nodes. They are responsible for notarizing the blocks onto the Bitcoin blockchain by sending transactions into the Bitcoin Network every 10 minutes. Komodo elects 64 notary nodes, although only 13 are necessary to secure the blockchain.
- Normal nodes. They are responsible for reading and validating transactions on the native chain.
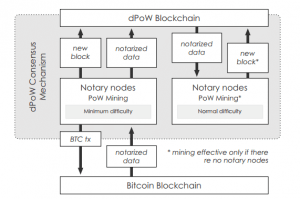
The benefit of the dPoW security is the ability to restore the network to its previous stage using the snapshots. The third party chains attached to the dPoW chain can reap the benefits of the Komodo network as they receive Bitcoin-level security without paying associated Bitcoin network fees for notarization transactions.
Jumblr
The Jumblr is an open-source cryptocurrency anonymizer. You can opt to use it whenever you transact via Komodo Platform. It costs approx. 0.3% KMD to send an anonymous transaction.
The Jumblr works in the following manner. It takes your KMD tokens from non-private address and sends them to a recipient via a cluster of untraceable ZK-SNARK addresses with zero-knowledge proofs. The Jumblr works with BarterDEX, too.
BarterDEX
BarterDEX is Komodo’s atomic-swap-powered decentralized exchange. While still in the testing phase, the exchange has already completed over 100,000 successful swaps. You can find its latest stats here.
The most notable features of the exchange are:
- Atomic swaps, which enable you to execute trades right out of your private wallet.
- Liquidity Multiplier for placing multiple orders for different coins using the same funds.
- Liquidity Provider nodes to cover low liquidity issues.
- Decentralized Ordering through a secure decentralized order book.
- Cross-chain compatibility including BTC and ETH protocol-based cryptocurrencies.
- Privacy and anonymity using zero-knowledge proof transactions.
- Users maintain their private keys.
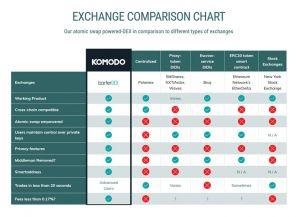
Here is a brief graph illustrating how it compares to other exchanges.
Decentralized Initial Coin Offers (dICOs)
Anyone can launch a blockchain and dICO using the Komodo Platform. Whatever coin you launch, it stays on a separate individual chain and is secured by the Komodo’s dPoW security.
Decentralized ICO’s make it easier and safer for investors to participate in crowdfunding campaigns. They are powered by the atomic swaps technology and use simple, wallet-to-wallet trades between different blockchains. Also, the investments can be made anonymous thanks to the Komodo’s Jumblr.
First dICO launched using Komodo’s dICO service was utrum (OOT). The project notably advertised its crowdfunding process as “grandma-friendly.” While traditional ICO’s usually limit the diversity of currencies available for funding, utrum’s dICO accepted more than 50 cryptocurrencies and had raised over a $1 million. As of January 2018, minimum seven projects have raised funds via Komodo’s dICO’s.
Peerchains
The Komodo Platform allows companies to have an independent blockchain. Such projects are granted free will to choose whether they want to upgrade together with the Komodo chain or they prefer not to inherit any new updates.
Such solution uses Merkle Trees(MoM), which notarize transactions on one chain onto others. Every chain processes transactions independently but all chains work in unison. As a result, the Komodo Platform can handle an extremely high volume of activities without experiencing network congestion. Current trial tests show Komodo is capable of handling more than 20,000 TPS. The future goal is to deliver 1 million TPS.
UXTO-Based Smart Contracts
Komodo’s smart contracts use Crypto-Conditions. They allow smart contracts to be developed on top of the Bitcoin-protocol-based blockchains. UTXO stands for Unspent Output of a Transaction.
At the moment, four Crypto-Conditions-based smart contracts are active on the Komodo Platform: Assets (for token creation); Faucet (for custom faucets); Rewards (for staking); and Dice (a dice game contract). Ultimately, Komodo developers seek to create an extensive library of smart contracts with adjustable specifications.
According to the developers, UXTO-based smart contracts have the following features:
- The smart contracts are a part of the Komodo code base and can be written in C and C++ programming languages.
- UTXO-based smart contracts are more reliable than balance-based smart contracts since entire balance of address is never at risk.
- UXTO smart contracts are the extension of the Bitcoin protocol, which makes them easy to implement and customize.
- They do not require GAS for executed processes.
- Crypto-Conditions support peer-to-peer zero-confirmation micropayments.
What Is Komodo (KMD) Coin?
KMD is the native coin of the Komodo Platform. It is mineable, and 200,000,000 KMD will be created in total. Like Zcash (ZEC) coins, KMD’s are mined using Equihash algorithm. At the moment, there are a little over 111,000,000 in circulation. It is estimated that Komodo will reach its total supply in the year 2030.
What Is The Use Case of Komodo (KMD) Coin?
Komodo (KMD) coin has the following use cases:
- Everyone who holds at least 10 KMD can earn 5% active user rewards.
- KMD can be used for instant, zero-confirmation swaps on Komodo’s DEX.
- KMD can be used as a go-between coin in trades which involve tokens that have no direct pairing on BarterDEX.
- KMD is used to pay for Komodo’s Blockchain Security Service.
- KMD powers UTXO-Based Smart Contracts.
- KMD is used to crowdfund dICO’s launched on the Komodo Platform. The holders can often enjoy early and discount offers.
- KMD supports Komodo’s Jumblr privacy feature.
Komodo ICO
Komodo’s ICO lasted from October 15 to November 20, 2016. One KMD was offered for 0.00012908222 BTC, so one could get 7747 KMD per 1 BTC. It was worth approx. $0.376 at the time.
The ICO was a success and raised 2639 BTC, which was nearly $2 million at the time. Exactly 100,000,000 KMD were issued during the crowdsale, and 90% of the coins were sold to investors. The remaining 10% were allocated to cover Komodo’s development and marketing costs.
The BTC raised during the ICO are used to cover BTC transaction costs, induced by the dPoW security mechanism.
How To Get 5% KMD Annual Rewards?
Anyone can stake KMD for 5% annual rewards. All you need to do is hold at least 10 KMD in a wallet which supports KMD. The rewards are paid out in KMD coins.
A surefire way to get the rewards is to store them in native Agama wallet. An alternative way is to use Ledger with Magnum Wallet, but mind that you will need to claim it manually.
Users cannot claim rewards if they keep KMD on exchanges or their KMD coins are inactive for more than a month.
Komodo (KMD) Mining
As mentioned above, Komodo employs Equihash mining algorithm. It makes it possible to mine KMD using both CPU and GPU. Approximately 1440 blocks are mined per day, and 75% of them are produced by Komodo Notary Nodes, leaving the remaining 25% to mining pools and solo miners. The block time is 60 seconds. It rewards 3 KMD per block.
Where To Buy Komodo (KMD)?
Instead of mining, you can buy Komodo (KMD) coins at the following exchanges.
Binance, CoinExchange (paired with BTC, ETH).
Bittrex, Satowallet Exchange, Crex24 (paired with BTC).
HitBTC (paired with BTC, ETH, USDT).
Cryptopia (paired with BTC, LTC, DOGE).
Upbit (paired with BTC, KRW).
Bitbns (paired with INR).
Digitalprice (paired with BTC, ETH, ARRR, VRSC, EMC2, DP, GAME, ZEX, TROLL, ZEC).
Komodo KMD Wallet
There are three popular options to store KMD coins. The project developers constantly upgrade the native multi-currency wallet Agama. You can download it for Windows, MacOS, Linux, Android, and iOS devices. The Agama wallet can also be used for staking KMD to receive 5% of the active user rewards.
If your Agama wallet address starts with Z, you should move your funds to another address before February 15, 2019. Z addresses will no longer be supported, so it is a mandatory thing to do.
Ledger hardware wallets support KMD, too. However, the company has issued a warning that Komodo KMD service will be disrupted after its hard fork on December 14, 2018. After the update, users cannot add new KMD accounts, check balance or send KMD. Whether the wallet will continue to support KMD depends on technical compatibility. One should wait for further announcements by Ledger and Komodo before storing KMD in Ledger wallets.
Last but not least, you can store KMD coins in a paper wallet. Here is a quick video guide on how to make one.
Komodo News, Progress, and Current State of the Project
Since the ICO, the Komodo Platform has achieved the following milestones (chronologically):
January 2017. Komodo launches mainnet, introducing dPoW consensus and independent asset chains. KMD coins were issued on January 31.
March 2017. Komodo develops the atomic swap protocol, which enables the trustless exchange of KMD coins.
July 2017. Komodo’s DEX carries out thousands of public atomic swaps.
August 2017. The Jumblr technology allows for private, zero-knowledge trades.
November 2017. The release of first GUI for atomic swaps trading.
January 2018. The release of Agama mobile wallet.
February 2018. A Public Stress Test reveals Komodo supported 13,900 atomic swaps in 48 hours.
March 2018. Komodo developers provide the interoperability solution which interconnects both Bitcoin-protocol-based coins and Ethereum-based ERC20 tokens. The Komodo Platform can now link 95% existing coins and tokens.
May 2018. The world’s first decentralized ICO (DICO) for utrum (OOT) is launched on the Komodo Platform.
June 2018. Beta version of HyperDEX, a new GUI for BarterDEX, is released.
July 2018. Komodo announces 2.0 platform features – Federated Multi-Chain Syncing and Cross-Chain Interoperability linking.
August 2018. Testing of UXTO Smart Contracts and Crypto-Conditions.
December 2018. Komodo’s Sapling upgrade successfully hard-forks more than 40 blockchains simultaneously.
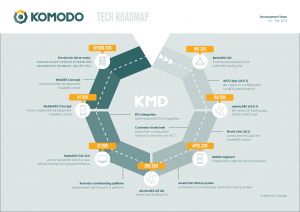
The project’s contributors are among the most active developers according to the CryptoMiso GitHub commits rankings. Also, they rank in the top ten most active blockchains in the world according to Blocktivity. Besides, the Komodo Platform is the Advanced Technology Partner with Amazon Web Services.
Currently, the development team focuses on improving several key elements of the Komodo Platform:
- Improving and adding new coins to the Agama wallet.
- Building BarterDEX 2.0, a more advanced version of the ecosystems’ decentralized exchange.
- Updating UTXO-based smart contract library for out-of-the-box enterprise solutions.
- Trying to achieve 1 million TPS for its Federated Multi-Chain Syncing scalability solution.
- Integrating more blockchains into the Komodo’s dPoW security service network.
- Enabling seamless migration of ERC20 tokens to the Komodo Platform.
In 2019 the project is expected to do a rebrand and release an updated roadmap. The rebrand focuses on updated messaging, improved user journey, brand new website, and product strategy.
Similar Projects
Waves (WAVES) – An open-source blockchain platform which allows users to launch custom crypto tokens.
Zcash(ZEC) – A privacy coin focused on delivering enhanced privacy and anonymity for transactions.
BitShares(BTS) – A platform which seeks to provide universal access to smart contracts.